What is THCa is a common question and we plan on having an answer to clear things up for you.
Understanding THCa in the Cannabis Plant: Legality, Effects, Extraction, and Benefits
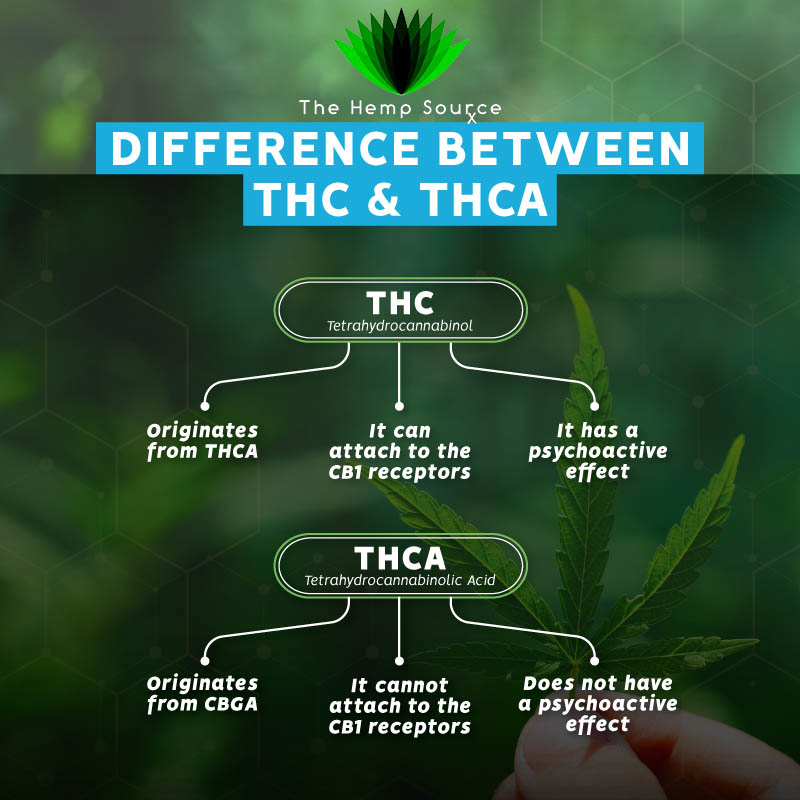
Cannabis, a plant that has been at the center of controversy and debate for decades, contains a variety of compounds known as cannabinoids. Among these cannabinoids, THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is most well-known for its psychoactive effects. However, another cannabinoid, THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid), is earning attention for its potential therapeutic benefits and unique properties. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what THCa is, its legal status, effects, extraction process, and its potential benefits.
So What is THCa?
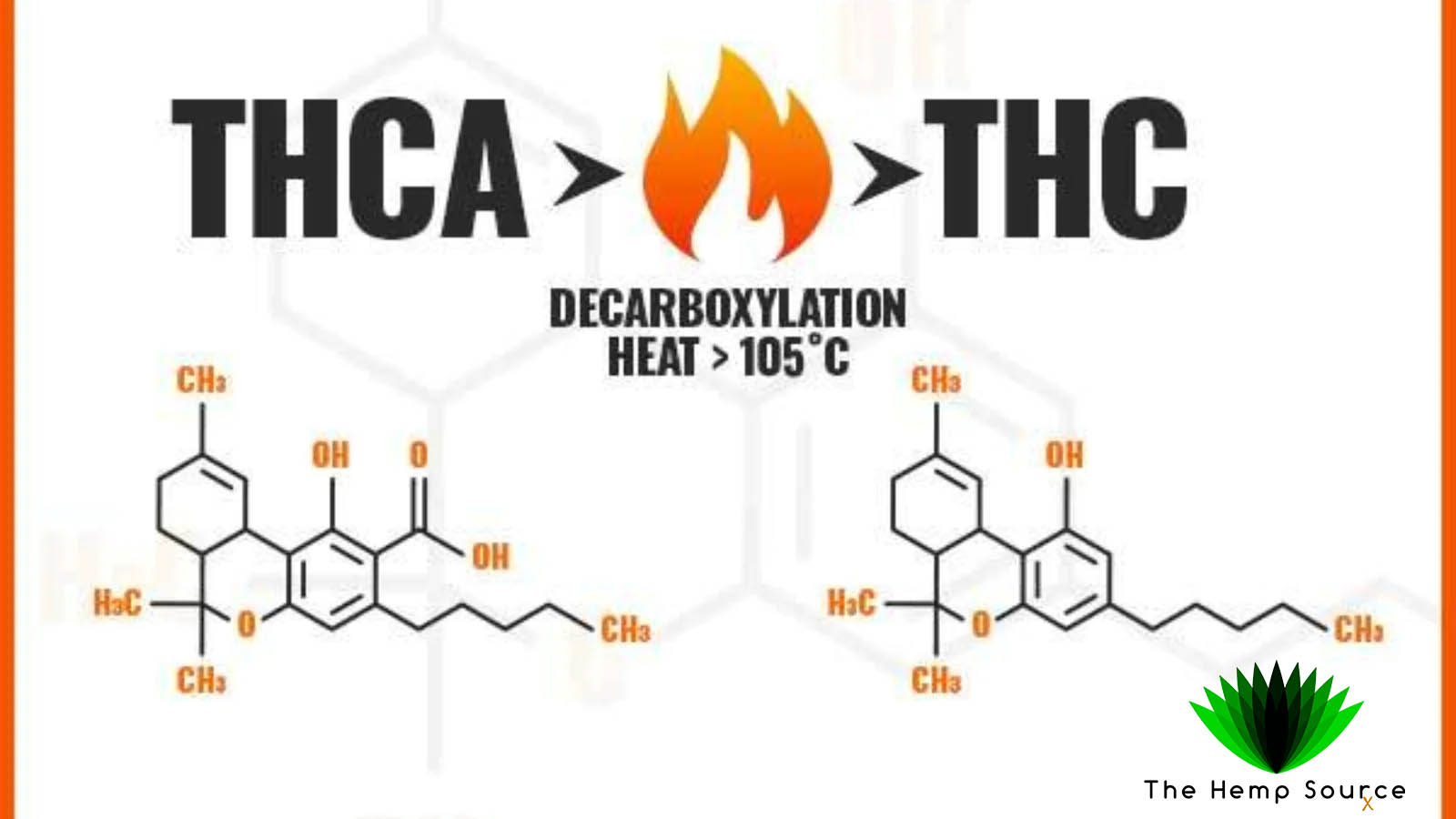
THCa is the acidic precursor to THC, found in raw and live cannabis plants. Unlike THC, THCa is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t produce the “high” commonly associated with cannabis consumption. When cannabis is harvested and dried, THCa slowly converts to THC through a process called decarboxylation, which involves the removal of a carboxylic acid group from the compound.
Legality of THCa
The legal status of THCa varies depending on jurisdiction and local laws. In many places where cannabis is legalized for medical or recreational use, THCa is treated similarly to THC. However, due to its non-psychoactive nature, THCa is often considered more “acceptable” in terms of legality.
In some regions, THCa extracts and products are legal as long as they contain minimal or no THC. It’s important to check local regulations and consult with legal professionals to ensure compliance with the law when dealing with THCa.
Effects of THCa
While THCa doesn’t produce psychoactive effects like THC, it has been studied for its potential therapeutic properties. Research suggests that THCa may have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antiemetic (anti-nausea) effects.
Some anecdotal reports and preliminary studies indicate that THCa may help with conditions such as:
- Chronic pain
- Inflammation
- Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
- Nausea and appetite stimulation
However, more research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of THCa and its effects on the human body.
Extraction Process of THCa
Extracting THCa from cannabis plants involves several methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The primary goal of extraction is to isolate THCa from other plant compounds to produce a concentrated form that can be used in various products.
Solvent-based Extraction: This method involves using solvents like ethanol, butane, or CO2 to extract THCa from the plant material. The solvent gets evaporated, leaving behind a concentrated THCa extract for your enjoyment. While effective, solvent-based extraction methods can be potentially dangerous if not done correctly, as solvents are flammable and can be hazardous.
Solventless Extraction: This method uses mechanical techniques such as ice water extraction or rosin pressing to separate THCa from the cannabis plant. Solventless extraction is considered safer and more natural but may yield lower quantities of THCa compared to solvent-based methods.
Decarboxylation: How THCa Converts to THC
Decarboxylation is a chemical process that involves the removal of a carboxylic acid group from a compound, in this case, from THCa to produce THC. This process occurs naturally over time when cannabis dries and ages, but it can also be accelerated by heating the cannabis plant material.
When cannabis is heated, either through smoking, vaping, or baking, the carboxylic acid group (the “A” in THCa) is removed from THCa, converting it into THC. This decarboxylation process unlocks the psychoactive properties of THC, allowing it to bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body and produce the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis consumption.
Ways to Decarboxylate THCa
Decarboxylation can be achieved through various methods, each with its own advantages and considerations:
Oven Decarboxylation:
- Process: Grind the cannabis buds into a coarse powder and spread them evenly on a baking sheet lined with parchment paper.
- Temperature: Preheat the oven to 220-240°F (105-115°C) and bake the cannabis for 30-45 minutes. Avoid exceeding 240°F (115°C) to prevent burning or degrading the cannabinoids.
- Advantages: Oven decarboxylation is a straightforward and accessible method that requires minimal equipment.
- Considerations: Monitor the temperature carefully to ensure consistent and even heating, and be cautious as the oven can produce strong odors.
Sous Vide Decarboxylation:
- Process: Place the ground cannabis in a vacuum-sealed bag or heatproof pouch and submerge it in a water bath.
- Temperature: Set the water bath to 200°F (93°C) and allow the cannabis to decarboxylate for 1-2 hours.
- Advantages: Sous vide decarboxylation allows for precise temperature control and can produce consistent results.
- Considerations: A sous vide machine is required, and the process can be time-consuming compared to other methods.
Decarboxylation with a Decarboxylator Device:
- Process: Utilize specialized decarboxylator devices designed specifically for cannabis decarboxylation.
- Temperature: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions, as temperature settings may vary between devices.
- Advantages: Decarboxylator devices offer convenience, ease of use, and precise temperature control.
- Considerations: The initial investment in a decarboxylator device may be higher than other methods, but it can be a worthwhile investment for frequent users.
Microwave Decarboxylation (Not Recommended):
- Process: Place the ground cannabis in a microwave-safe dish and microwave on a low setting in short intervals, checking and stirring frequently.
- Temperature: Use the lowest power setting to avoid overheating and degrading the cannabinoids.
- Considerations: Microwave decarboxylation can be inconsistent and may result in uneven heating or overheating, leading to reduced potency and quality of the final product. This method is not recommended for optimal decarboxylation.
Benefits of THCa
The potential benefits of THCa are still being explored, but some of the most promising areas of research include:
- Pain Management: THCa has shown promise in alleviating chronic pain, making it a potential alternative to traditional painkillers.
- Inflammation Reduction: THCa has anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other inflammatory disorders.
- Neuroprotection: Preliminary studies suggest that THCa may help protect brain cells from damage and degeneration, offering potential therapeutic benefits for neurodegenerative diseases.
- Nausea Relief: THCa has been studied for its antiemetic effects, making it a potential treatment for nausea and vomiting, especially in chemotherapy patients.
Conclusion
THCa, the non-psychoactive precursor to THC found in raw cannabis plants, is gaining recognition for its potential therapeutic benefits. While the legal status of THCa varies, it is generally considered more acceptable than THC due to its non-psychoactive nature. The extraction of THCa involves various methods, each with its advantages and challenges, and ongoing research continues to explore its potential benefits for pain management, inflammation reduction, neuroprotection, and nausea relief.
As with any cannabis-derived product, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals and adhere to local laws and regulations when considering THCa for therapeutic use. While promising, more research is needed to fully understand the effects and potential benefits of THCa on human health.